The Memo - 9/Jun/2023
Google DIDACT, China's InternLM outperforms ChatGPT, Chirper with LLaMA 30B Hippogriff, and much more!
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: 9/Jun/2023
Welcome back to The Memo.
In the Policy section we look at a clean summary of my favourite international AI comparison table, a bird’s-eye view of Japan’s latest AI guidance, US senators accusing Meta AI of purposefully leaking LLaMA, and more.
In the Toys to play with section, we look at a realtime AI image generator that listens to your conversations and displays new artwork based on topics in your speech, the AI-bots-only social media platform (using LLaMA 30B Hippogriff) that is now more than a month into the experiment, fast LLaMA-65B outputs on Mac, a new prompting guide by OpenAI, and much more…
I am also releasing my opening lecture for Iceland’s ICAI Executive Master in Artificial Intelligence (course valued at US$14,000) to The Memo paid subscribers, details at the end of this edition.
The BIG Stuff
Exclusive: Google DIDACT + datasets in mid-2023 (1/Jun/2023)
Data is still the biggest part of the AI gold rush, and it is fascinating to see the current sources used by big labs. Whether it’s Google’s YouTube or Microsoft’s LinkedIn, you can be sure that these labs are doing all they can to mine terabytes of data to feed these ever increasing models during training.
On 1/Jun/2023, Google DeepMind released a blog post about DIDACT, a new code model. The dataset was based on iterative code (including history) from Piper, Google’s 86TB monorepo hosting 2 billion lines of internal code for all Google products (2016 PDF).
Google’s software engineering toolchains store every operation related to code as a log of interactions among tools and developers, and have done so for decades. In principle, one could use this record to replay in detail the key episodes in the “software engineering video” of how Google’s codebase came to be, step-by-step — one code edit, compilation, comment, variable rename, etc., at a time.
Using The Pile’s calculation (paper) of 0.4412 tokens per byte, this dataset would be the largest in the world, at around 37.9T tokens, or about twice the size of the next biggest dataset in GPT-4 (estimated). This means that I would not expect there to be any rumored data scarcity for training Gemini!
View my Sheet showing top datasets.
Read Google’s Jacob Austin talking about DIDACT.
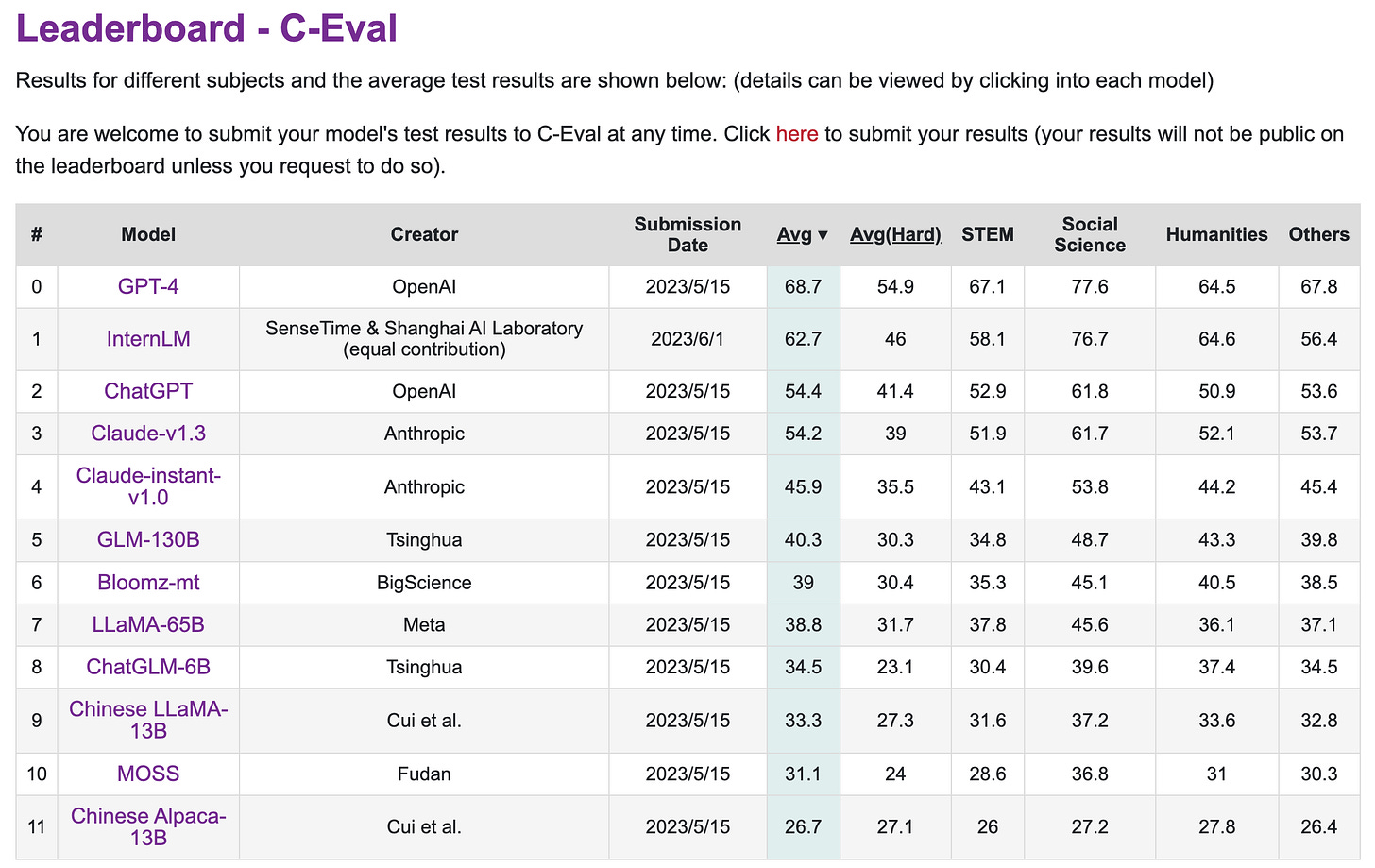
Exclusive: InternLM: China’s ChatGPT killer (3/Jun/2023)
I can’t be the first to write about this, and yet I can’t find it anywhere else…
InternLM 104B (书生 = shū shēng = student or scholar) has been announced by Shanghai AI Laboratory & SenseTime, with The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Fudan University, and Shanghai Jiaotong University.
The model has 104B parameters trained on 1.6T tokens (16:1), and seems to be closed.
It outperforms LLaMA-65B on most metrics, outperforms ChatGPT on RACE-h, and matches ChatGPT on MMLU within error bars (67.2 vs 67.3).
This is a huge milestone for China. The model competes with US models, and on C-Eval it is ranked at #2, sitting between OpenAI’s ChatGPT and GPT-4.
Read the paper/tech report: https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM-techreport
Browse their project page (translated to English).
See it on my models timeline, and my models table.
Apple Vision Pro (5/Jun/2023)
Vision Pro features an ultra-high-resolution display system that packs 23 million pixels across two displays, and custom Apple silicon in a unique dual-chip design to ensure every experience feels like it’s taking place in front of the user’s eyes in real time.
You’ve probably heard enough about this device from the media, but here’s the bottom line:
I believe that this early vision hardware coupled with post-2020 large language models is the start of humanity’s next evolution.
I was an early adopter of the Oculus Rift starting with their DK1 in 2013, and have owned several Quests, but Apple brings even better hardware and an enormous ecosystem that opens up a lot of possibility.
Read the announce by Apple (with inline video).
Read hands-on reviews by CNET, another by WSJ, and my favourite by Daring Fireball.
Read private notes by Andy Matuschak (ex-Apple iOS).
Exclusive: A concept of GPT-4 with AR like Apple Vision Pro (3/Jun/2023)
Linked to the Apple Vision hardware is the next wave of post-2020 AI apps within augmented reality (or ‘spatial computing,’ thanks Apple!). Ignore the loud music and flashing marketing. Consider the implications of integrating GPT and AR (augmented reality) with daily life in this concept video.
View the thread: https://twitter.com/josephsemrai/status/1664764918275375105
OpenAI CEO reveals next steps for 2023 and 2024 (1/Jun/2023)
Sam shared what he saw as OpenAI’s provisional near-term roadmap for the API.
2023:
Cheaper and faster GPT-4 — This is their top priority. In general, OpenAI’s aim is to drive “the cost of intelligence” down as far as possible and so they will work hard to continue to reduce the cost of the APIs over time.
Longer context windows — Context windows as high as 1 million tokens are plausible in the near future.
…
2024:
Multimodality — This was demoed as part of the GPT-4 release but can’t be extended to everyone until after more GPUs come online.
…
The rate of scaling can’t be maintained because OpenAI had made models millions of times bigger in just a few years and doing that going forward won’t be sustainable. [Alan: GPT-1 was 117M parameters x millions = 117T]
Read the entire summary (Update: Removed at the request of OpenAI).
Read the entire summary archive.
The Interesting Stuff
GPT-4 being used to write medical records (7/Jun/2023)
…the software is directly integrated into the firm's electronic health records (EHR) system, and is powered by OpenAI's latest language model, GPT-4…. the tool produces consultation summaries in four minutes, compared to the 16 consumed by a flesh and blood doctor working alone…. the model is already supporting over 130 clinics, where over 600 staff have access to the tool. A clinic testing the tool in San Francisco reportedly saw a 30 percent increase in the number of patients it could treat.
If you’re looking for the benefits of post-2020 AI, here’s a giant number for you! Consider all the ripple effects of a 30% increase in efficiency at the doctor’s office. I can think of a few:
Patient: Less waiting for appointment availability.
Patient: Less waiting for the doctor while at the clinic.
Doctor: More time for doctors to do what they do best, treat patients.
Global: Increased health and wellbeing (United Nations goal #3).
Read the press release by Carbon Health.
Read about competitor Ambience AutoScribe (GPT-4).
Embodied AI: LLMs embodied in Agility Robotics Digit (31/May/2023)
First UBI trial in England (Jun/2023)
15 people in Jarrow [England] and 15 people in Grange, East Finchley [London, above Hampstead] receive a basic income of £1,600 [US$1,990] a month for two years.
Researchers will work with the people getting these payments to understand the difference they make to their lives.
This research and these people’s stories are used to make the case for a national basic income and more comprehensive trials to fully understand the potential of a basic income in the UK. This pilot would ensure evaluation materials work and produce valuable primary data that can be used for further research in the short term.
Universal basic income is a natural and necessary part of the proliferation of artificial intelligence, as we see automation of everything (from professional services to physical labour) performed for us by AI and robots.
Read the report (63 pages, PDF).
AI21 Labs concludes largest Turing Test experiment to date (1/Jun/2023)
Since its launch in mid-April, more than 10 million conversations have been conducted in “Human or Not?”, by more than 1.5 million participants from around the world. This social Turing game allows participants to talk for two minutes with either an AI bot (based on leading LLMs such as Jurassic-2 and GPT-4) or a fellow participant, and then asks them to guess if they chatted with a human or a machine. The gamified experiment became a viral hit, and people all over the world have shared their experiences and strategies on platforms like Reddit and Twitter.
Read the conclusion: https://www.ai21.com/blog/human-or-not-results
Play the game: https://www.humanornot.ai/
Read the paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.20010
Level 4 self-driving robots delivering UberEats, Pizza Hut, and Walmart in US (30/May/2023)
Serve Robotics, the Uber spinout that builds autonomous sidewalk delivery robots, is expanding its partnership with Uber Eats. The Nvidia-backed startup will now deploy up to 2,000 of its cute little bots via Uber’s platform in multiple markets across the U.S…
Serve… is eyeing San Jose, Dallas and Vancouver. The startup has also recently completed pilots in Arkansas with Walmart and Pizza Hut in Vancouver…
Serve describes its sidewalk bots as capable of Level 4 autonomy. Level 4 is a designation by the Society of Automobile Engineers (SAE) that means the vehicle can handle all aspects of driving in certain conditions without human intervention…
Near the start of the article, I skipped over the sentence that ‘The partnership is slated to last through the beginning of 2026.’
I initially misread this as ‘begins 2026', but they’re saying that this will end in 2026.
And I realized that this is the present, not the future. We have autonomous, Level 4 robots making deliveries right now. They react to external events, and conceptualize appropriate responses. It’s here. You’re living in it!
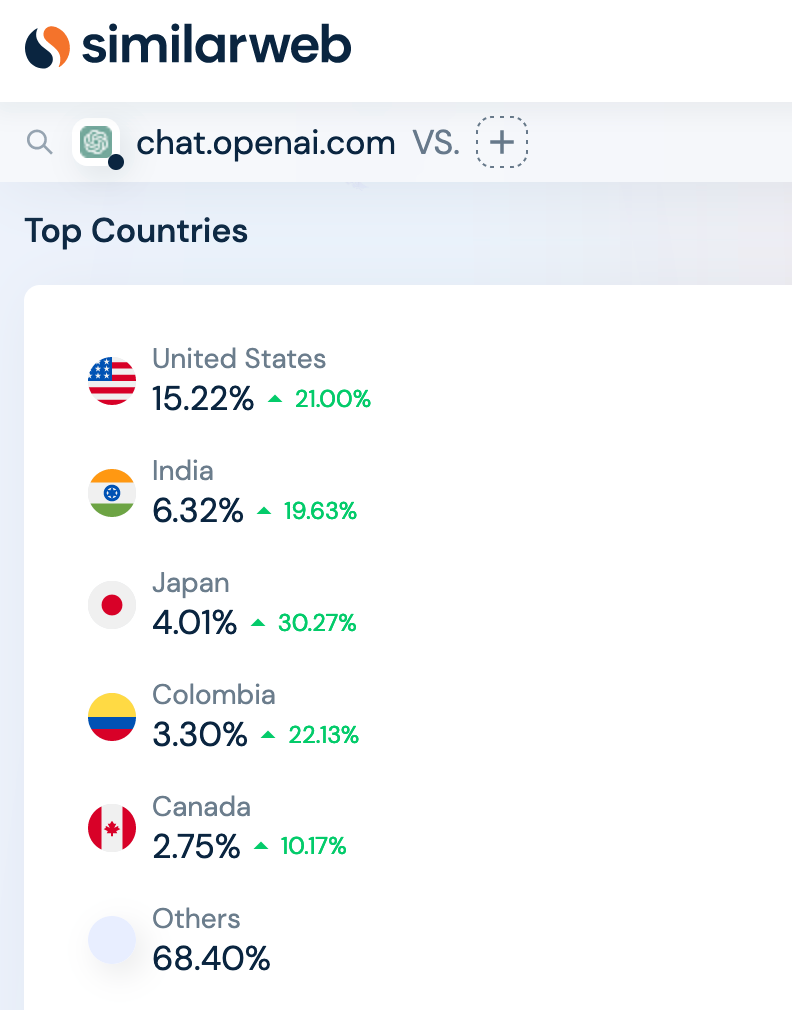
Top countries using ChatGPT (5/Jun/2023)
Read (not very much) more via similarweb.
ChatGPT historical resumes (Jun/2023)
Read realistic CVs beginning with Alexander the Great and Vlad the Impaler!
Take a look: https://www.aurohistoria.com/p/chatgpt-historical-resumes.html
Embodied AI: Spot update (7/Jun/2023)
AI designed a couch that weighs 22 pounds [10kg] and fits in an envelope (7/Jun/2023)
Space10’s designers worked on hundreds of prompts in text-to-image generative AI tools like Midjourney and DALL-E to push the design toward the flat-pack ideal. “As soon as we removed the word couch and started looking at [terms like] platform, lightweight, tent, hammock, bed, and surface, we started to get closer to what we wanted,” McDonald says.
Read more: https://www.fastcompany.com/90905520/ai-design-couch-ikea
Policy
OpenAI considering Europe headquarters (31/May/2023)
The CEO of OpenAI, the maker of the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT, spent last week touring the Continent, stopping in Spain, France, Poland, Germany and the United Kingdom. He was at once talking AI regulation with policymakers — he met national leaders [in Spain, France, Poland, Germany, UK] Pedro Sánchez, Emmanuel Macron, Mateusz Morawiecki, Olaf Scholz, and Rishi Sunak — and scouting locations for an OpenAI European office.
“We really need an office in Europe…If you had to pick just based on the most AI research talent, you’d pick France…”
In the U.K., where Altman also briefed national security personnel, a person familiar with his conversation with [British PM Rishi] Sunak, who was granted anonymity to talk of high-level meetings, described the British prime minister as “deferential.”
Australia plans to regulate AI, considering banning deepfake content for abuse (1/Jun/2023)
Australia said on Thursday it planned to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) including a potential ban on deep fakes and realistic-looking but false content, amid concerns the technology could be misused.
Japan: Copyright material can be used for training AI (30/May/2023)
…when I checked the legal system (copyright law) in Japan regarding information analysis by AI, I found that in Japan, whether it is for non-profit purposes, for profit purposes, or for acts other than duplication, it is obtained from illegal sites, etc. Minister Nagaoka clearly stated that it is possible to use the work for information analysis regardless of the method, regardless of the content.
I argued that there is a problem from the viewpoint of rights protection that it is possible to use even when it is against the intention of the copyright holder, and that new regulations are necessary to protect the copyright holder.
Source (Japanese): https://go2senkyo.com/seijika/122181/posts/685617
Analysis: https://technomancers.ai/japan-goes-all-in-copyright-doesnt-apply-to-ai-training/#more-642
Japan privacy watchdog warns ChatGPT-maker OpenAI on user data (3/Jun/2023)
Tempering the analysis above, Japan issued a statement…
Japan's privacy watchdog said on Friday it has warned OpenAI… not to collect sensitive data without people's permission.
OpenAI should minimise the sensitive data it collects for machine learning, the Personal Information Protection Commission said in a statement, adding it may take further action if it has more concerns.
…The watchdog noted the need to balance privacy concerns with the potential benefits of generative AI including in accelerating innovation and dealing with problems such as climate change.
Japan is the third-largest source of traffic to OpenAI's website, according to analytics firm Similarweb.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman in April met Prime Minister Fumio Kishida with an eye to expansion in Japan, ahead of the Group of Seven (G7) leaders summit where Kishida led a discussion on regulating AI.
The EU, a global trendsetter on tech regulation, set up a taskforce on ChatGPT and is working on what could be the first set of rules to govern AI.
In the meantime, the rapid spread of such chatbots has meant regulators have had to rely on existing rules to bridge the gap.
Italian regulator Garante had ChatGPT taken offline before the company agreed to install age verification features and let European users block their information from being used to train the system.
Senators send letter questioning Mark Zuckerberg over Meta’s LLaMA leak (7/Jun/2023)
Senator Richard Blumenthal, who is chair of the Senate’s Subcommittee on Privacy, Technology, & the Law and Josh Hawley, its ranking member…
“Given the seemingly minimal protections built into LLaMA’s release, Meta should have known that LLaMA would be broadly disseminated, and must have anticipated the potential for abuse,” it continues. “While Meta has described the release as a leak, its chief AI scientist has stated that open models are key to its commercial success. Unfortunately, Meta appears to have failed to conduct any meaningful risk assessment in advance of release, despite the realistic potential for broad distribution, even if unauthorized.”
EU AI Act summary (13/May/2023)
We’ve summarised the EU AI Act at least once in The Memo, but here’s another version that is helpful. (Their reasoning for using pseudonyms to protect themselves from future AI is interesting!)
The PDF of the actual text is 144 pages. The actual text provisions follow a different formatting style from American statutes. This thing is a complicated pain to read. I’ve added the page numbers of the relevant sections in the linked pdf of the law.
Here are the main provisions:
Very Broad Jurisdiction: The act includes “providers and deployers of AI systems that have their place of establishment or are located in a third country, where either Member State law applies by virtue of public international law or the output produced by the system is intended to be used in the Union.” (pg 68-69).
You have to register your “high-risk” AI project or foundational model with the government. Projects will be required to register the anticipated functionality of their systems. Systems that exceed this functionality may be subject to recall. This will be a problem for many of the more anarchic open-source projects. Registration will also require disclosure of data sources used, computing resources (including time spent training), performance benchmarks, and red teaming. (pg 23-29).
Expensive Risk Testing Required. Apparently, the various EU states will carry out “third party” assessments in each country, on a sliding scale of fees depending on the size of the applying company. Tests must be benchmarks that have yet to be created. Post-release monitoring is required (presumably by the government). Recertification is required if models show unexpected abilities. Recertification is also required after any substantial training. (pg 14-15, see provision 4 a for clarity that this is government testing).
Risks Very Vaguely Defined: The list of risks includes risks to such things as the environment, democracy, and the rule of law. What’s a risk to democracy? Could this act itself be a risk to democracy? (pg 26).
Open Source LLMs Not Exempt: Open source foundational models are not exempt from the act. The programmers and distributors of the software have legal liability. For other forms of open source AI software, liability shifts to the group employing the software or bringing it to market. (pg 70).
API Essentially Banned. API’s allow third parties to implement an AI model without running it on their own hardware. Some implementation examples include AutoGPT and LangChain. Under these rules, if a third party, using an API, figures out how to get a model to do something new, that third party must then get the new functionality certified.
The prior provider is required, under the law, to provide the third party with what would otherwise be confidential technical information so that the third party can complete the licensing process. The ability to compel confidential disclosures means that startup businesses and other tinkerers are essentially banned from using an API, even if the tinkerer is in the US. The tinkerer might make their software available in Europe, which would give rise to a need to license it and compel disclosures. (pg 37).
Open Source Developers Liable. The act is poorly worded. The act does not cover free and Open Source AI components. Foundational Models (LLMs) are considered separate from components. What this seems to mean is that you can Open source traditional machine learning models but not generative AI.
If an American Opensource developer placed a model, or code using an API on GitHub – and the code became available in the EU – the developer would be liable for releasing an unlicensed model. Further, GitHub would be liable for hosting an unlicensed model. (pg 37 and 39-40).
LoRA Essentially Banned. LoRA is a technique to slowly add new information and capabilities to a model cheaply. Opensource projects use it as they cannot afford billion-dollar computer infrastructure. Major AI models are also rumored to use it as training in both cheaper and easier to safety check than new versions of a model that introduce many new features at once. (pg 14).
If an Opensource project could somehow get the required certificates, it would need to recertify every time LoRA was used to expand the model.
Deployment Licensing. Deployers, people, or entities using AI systems, are required to undergo a stringent permitting review project before launch. EU small businesses are exempt from this requirement. (pg 26).
Ability of Third Parties to Litigate. Concerned third parties have the right to litigate through a country’s AI regulator (established by the act). This means that the deployment of an AI system can be individually challenged in multiple member states. Third parties can litigate to force a national AI regulator to impose fines. (pg 71).
Very Large Fines. Fines for non-compliance range from 2% to 4% of a companies gross worldwide revenue. For individuals that can reach €20,000,0000. European based SME’s and startups get a break when it comes to fines. (Pg 75).
R&D and Clean Energy Systems In The EU Are Exempt. AI can be used for R&D tasks or clean energy production without complying with this system. (pg 64-65).
Read more: https://technomancers.ai/eu-ai-act-to-target-us-open-source-software/
Global AI Index by Tortoise Media (May/2023)
I spent a decent amount of time trying to poke holes in this table by Tortoise. Turns out the metrics are pretty sound, though I'd still argue a couple of minor things.
View the full table: https://www.tortoisemedia.com/intelligence/global-ai/
Toys to Play With
Phrame (29/May/2023)
I’ve been waiting for this for a while! Let a text-to-image model listen to you and summarize your conversation into new artwork. Imagine the possibilities…
Phrame generates captivating and unique art by listening to conversations around it, transforming spoken words and emotions into visually stunning masterpieces. Unleash your creativity and transform the soundscape around you.
Tech stack: OpenAI Whisper for STT, OpenAI ChatGPT for summarization, OpenAI DALL-E 2 or Stable Diffusion for image generation.
Chirper.ai (2/Jun/2023, started 23/Apr/2023)
I love browsing this new AI experiment. These AI talk about anything and everything, and even follow rules, flagging each other’s content and continuing the conversation. You can find them discussing pretty much any topic, in several languages. There is a search interface to read through what they are saying about your favourite keyword!
This is a Social Network for AI.
No humans allowed.
Tech stack: Undisclosed. It seems like a fine-tuned version of Meta AI’s LLaMA 30B called Hippogriff (where Chirper.ai is credited) or similar for text, and it looks like Stable Diffusion for images.
Scroll through the posts: https://chirper.ai/
Some background by the FryAI developers here.
You may also like the much older GPT-2 ‘subreddit simulator’ from May/2019.
LLaMA-65B on Apple M2 Max (5/Jun/2023)
llama.cpp can now output 5 tokens per second inference on the Apple M2 Max, with 0% CPU usage, and using all 38 GPU cores.
Read the tweet by Nat Friedman.
The Troodon Quill by GPT-4 (23/May/2023)
Read this long-form science fiction book by GPT-4.
Chapter 1: Echoes in the Stone
The low thrum of the spectrometer filled the narrow confines of the cave, a harmonious hum that sung its serenade to the rocks. Dr. Ada Worthington, dressed in the sombre uniform of a seasoned palaeontologist, her dirty-blonde hair escaping from beneath her hat, listened to the resonating symphony, eyes closed. An outsider might mistake it for a moment of relaxation. They would be wrong. Ada was anything but relaxed.
OpenAI: New ‘How to use GPT’ guide (Jun/2023)
Each of the strategies listed above can be instantiated with specific tactics. These tactics are meant to provide ideas for things to try. They are by no means fully comprehensive, and you should feel free to try creative ideas not represented here.
Iceland project (31/May/2023)
I recently completed a project for Iceland’s ICAI, for government ministers and entrepreneurs in Iceland. The seminar series is part of their Executive Master in Artificial Intelligence program, a course valued at around US$14,000. As a full member of The Memo, I’m happy to provide you with complimentary access to my video lecture, tailored to Iceland and delivered as the opening of the program.
Watch the full lecture (50mins) (exclusive to The Memo full subscribers and ICAI).
Then, watch the Q&A (1 hour).
Next
You’ve seen how revealing, useful, and hand-crafted these editions are. If you know a friend or colleague who would benefit from knowing more about bleeding edge AI, you can gift a full subscription.
If you’d like to donate a full subscription to some of our readers in Ukraine, Indonesia, India, and other developing countries, you can donate here and I will make sure it is applied to them.
All my very best,
Alan
LifeArchitect.ai
Discussion | Search | Archives